IVLP
About
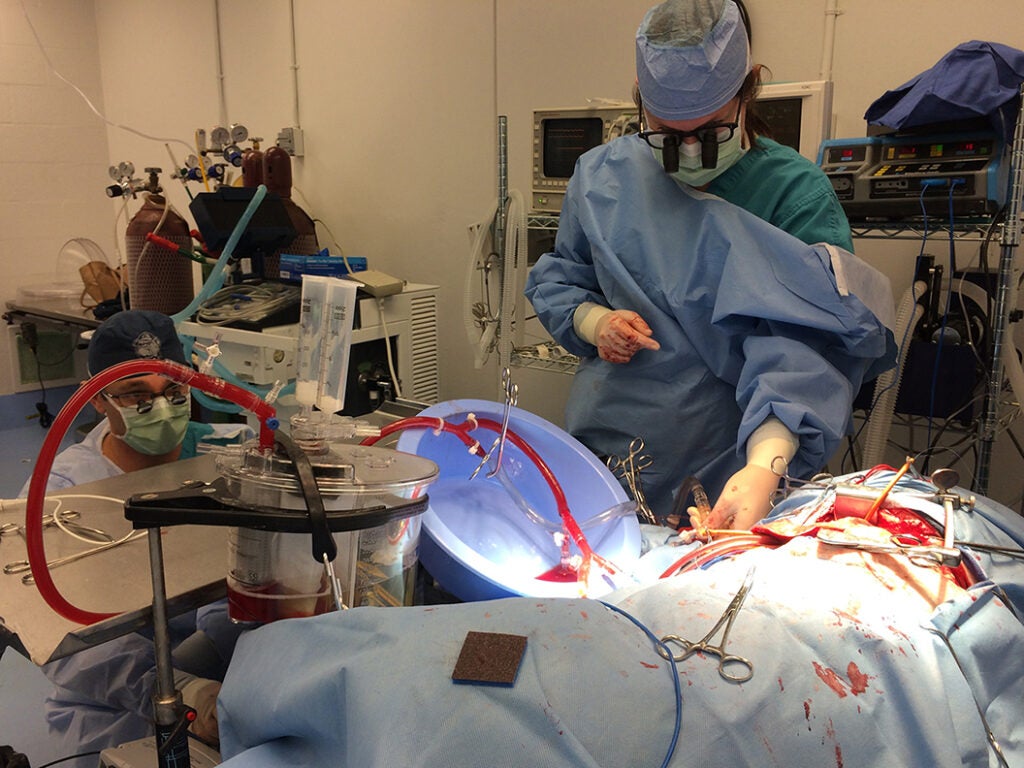
The use of ex vivo lung perfusion (EVLP) has demonstrated significant potential to assess donor lungs for transplantation and is being used clinically with success. Our lab has advanced this technique, demonstrating successful rehabilitation of porcine lungs for transplantation using targeted drug therapy during EVLP. Based on our prior success with EVLP, we have designed a novel technique for the perfusion of lungs in vivo (in vivo lung perfusion, IVLP) with Steen solution (as used for EVLP) in a preclinical porcine model, which allows for targeted lung rehabilitation and demonstrates proof-of-concept. IVLP involves cannulation of the pulmonary artery (inflow) and pulmonary veins (outflow) to the injured lung to enable closed-circuit perfusion and direct treatment. By combining the benefits of ECMO and EVLP, IVLP provides an isolated platform upon which injured lungs can be treated in vivo with targeted therapies while mitigating the risks and limited efficacy of systemic treatment.
Currently, no methods exist for targeted treatment for the rapid rehabilitation of lungs affected by acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Clinically, we foresee IVLP as a totally percutaneous intervention to function as an adjuvant to ECMO therapy to shorten duration of support resulting in reduced morbidity and mortality. This could be transformational in the treatment of ARDS.
We have shown that 4 hours of IVLP successfully rehabilitated LPS-injured lungs compared to ECMO support alone in this preclinical porcine model. Mehaffey et al. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 155(1):440-448.e2, 2018. [Link] We have also recently shown that 2 hours of IVLP demonstrated superior lung function in this preclinical model of sepsis-induced ARDS. Byler et al. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 34(1):337-346, 2022. [Link]